As the electric vehicle revolution continues to unlock new possibilities for drivers across the globe, one of its most beloved features is the convenience of EV charging stations. These innovative access points allow drivers to “refill” their cars with electricity, just like a gas station pumps fuel. With more and more charging stations popping up around the world, it’s becoming easier to charge up and hit the road for a long-distance drive. Not only are these stations convenient, but they offer an environmentally-friendly way to power electric cars. So, whether you’re planning a cross-country jaunt or just need a quick pit stop, an EV charging station is your ticket to freedom!
The three main types of EV charging stations all have their advantages and disadvantages.
These charging station types go by the following names:
- Level 1 (Private)
- Level 2 (Private or Public)
- Level 3 or DC Fast Charging (Public)
Every station has benefits and specific purposes. In the section below, we will go into more depth for each option so you can better understand which EV charging station works best for your individual needs.
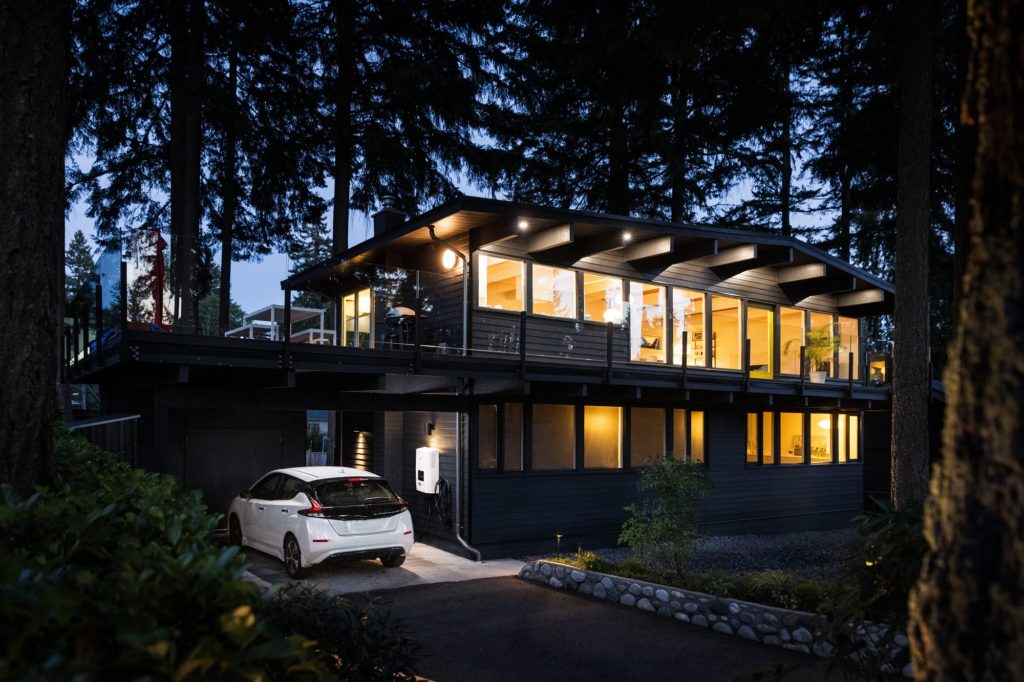

EV Charging Station at Home
Can you bring the convenience of EV charging to your own home? With some simple preparation, it’s possible to install an EV charging station in your garage or driveway and power up with ease. From deciding on the right equipment for your car to selecting the best installation option for your property, here’s how you can get the most out of EV home charging.
The first step to setting up a home charging station is selecting the right equipment for your vehicle. The type of charger you’ll need will depend on two factors: the kind of car you drive and how much power it needs to charge. There are different levels of chargers available, so it’s important to do your research before selecting the right one for your car.
For drivers of plug-in hybrid models, Level 1 chargers will usually suffice. These basic units require a standard outlet and don’t need to be installed. However, if you have a fully electric car, you’ll likely need to install a Level 2 charger to get the most out of your home charging station.
Level 1 Charging Stations
There are a few 120V outlets, however, by far the most common is the NEMA 5-15 and NEMA 6-15. The typical household outlet is the “shocked-face thing” you have seen for your entire life. It has been by your side (literally) when you need it most.
NEMA is the acronym for National Electric Manufacturers Association. The first set of digits is the outlet class (6) and the second set is the maximum current (15 amps).
NEMA 5-15 is limited to 15A, 125V and NEMA 6-15 is limited to 15A, 240V
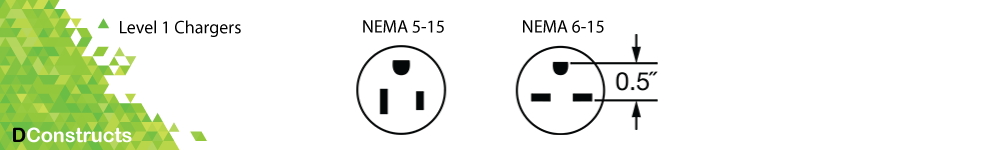
Level 1 charging cables typically come with your vehicle when you purchase it, and they can plug into a standard wall outlet. Such chargers deliver 1.4 kW of charge, providing 4 miles of driving range per hour of charging. That means it usually takes 35-50 hours to fully charge your vehicle depending on your car battery size. If you only drive a short distance each day, then this may work for you. But, if you find yourself driving more often or needing to be fully charged throughout the day, this method can take too long.
Recommended Level 1 Hardware
- Budget – 15A Charging Cable – Besenergy Level 1 EV Charger
- Flexible – 16A Level 1/2 Charging Cable – Schumacher SC1455 Level 1 and Level 2 Portable EV Charger
- Miscellaneous – SAE J1772 to Tesla Adaptor
Level 2 Charging Stations
The next step up, Level 2 chargers are the most recommended type of charger to have at home. These chargers typically require professional installation and a dedicated circuit. Level 2 chargers deliver between 3-7 kW of charge, providing 20-30 miles of driving range per hour of charging. With this option, you can fully charge your vehicle in approximately 8 hours.
Level 2 chargers come in two different styles: either hardwired or plugged into a 240V outlet. If you don’t have a 240V outlet readily available, one can be pulled from your electrical panel. It is highly recommended to hire a certified electrician to do this work.
The most popular 240V outlets for the EV charging stations are NEMA 14-30 and NEMA 14-50, delivering 30A and 50A of current respectively. There are other less common outlets that are acceptable for EV charging such as NEMA 6-30, NEMA 6-50, NEMA 10-30, NEMA 10-50
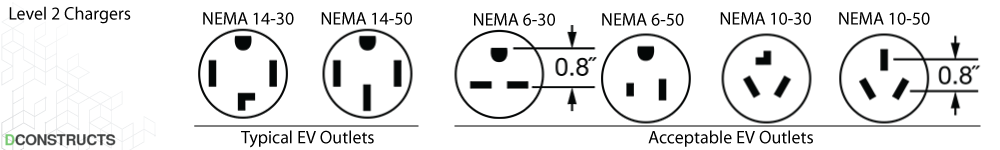
Recommended hardware
- Budget – 32A Charging Cable – VEVOR Level 2 EV Charger, 32 Amp 110-240V
- Fastest – 50A Charging Station – ChargePoint Home Flex Electric Vehicle (EV) Charger
- Outdoor – 40A Charging Station – Grizzl-E New Level 2 Smart EV Charger
- Miscellaneous – SAE J1772 to Tesla Adaptor
Pro Tip: Consider a proper backup generator will be useful in charging your vehicle in case of a power grid emergency shut down.
Public EV Charging Stations
For those who don’t have the luxury of having their home charging station, there are plenty of public EV charging stations around to make life easier.
Level 2 charging stations are still common in public places like parking lots, shopping centres and garages. The next level up from a Level 2 charger is a Level 3, which will fill your EV much quicker.
Level 3 Charging Stations
Level 3 charger (also referred to as DC Fast Chargers) is the fastest EV Charging Station on the market. When you need to quickly charge your car and continue on your road trip, a level 3 charger is the best option. Compared to other chargers, a level 3 charger can transfer the most amount of power and charge in the quickest amount of time. If you use a level 3 charger, it will take about 40 minutes to charge your vehicle up to 80%. At the same time , if you want to wait until it’s fully charged, the last 20% will take an additional hour. Level 3 chargers are only found in commercial and public use because they’re expensive to install and require large amounts of energy.
While all EV charger types being able to charge a battery to full within an hour would be amazing, the faster the charger is, the more electricity it requires. Level 3 chargers need way too much power for localized circuits like homes and businesses and are not supported by them. Level 3 chargers, on the other hand, are available more frequently along highways and roads as they become a part of the local infrastructure – similar to how gas stations are typically found.
A final note on the charge times
Rechargeable batteries for electric cars have the same safeties as all other types of batteries to prevent overcharging. After the battery reaches 80% capacity, it will start trickle charging. This means that at 80%, all three levels of charge will progress at a slow speed by design. Therefore, many Level 3 charging stations automatically turn off once the battery hits 80%. If you’re looking to rapid charge for a long-distance trip, keep in mind that “fully charged” may not actually mean 100%, and plan your recharge time accordingly.
Pro Tip: If you're looking to fill up your vehicle with a charging cable locked in, we've listed a few recommended products below.
How to find public EV charging stations?
Finding public EV charging stations is quite simple. Most cities have websites that list all the charging locations around town as well as online maps and apps like PlugShare, OpenChargeMap, and ChargeHub which also allow you to search by location. Some car manufacturers like Tesla and Rivian have sophisticated built-in software that helps locate the charging stations. This feature makes planning a road trip much less stressful.
You can find chargers in a variety of places such as gas stations, shopping centers, airports, and even at some hotels. Even though the charging station locations are increasing daily, they still aren’t as plentiful as gas stations so it is important to plan your trips ahead of time.
Recommended hardware
- Tesla Model 3/Y Charger Lock for J1772 Adapter
- Tesla Charging Adapter with a lock Compatible with Tesla Model 3, Y, S, X
- Adaptor for standard electric vehicles to connect to Tesla chargers
EV Charging Stations Costs
The final cost for an EV Charging Station will depend on several factors. The location you choose to install the charger, the type of charger and any additional services needed. An outlet suitable for a Level 1 charger is most likely already installed in your garage. Installing a Level 2 charger in your garage may cost anywhere from $1,000 – $2,000 depending on the complexity and materials used.
For public charging stations, the cost is typically much higher due to infrastructure and installation costs. Level 3 chargers can cost upwards of $20,000 to $150,000+ making the installation for private use not realistic. For 99% of the use cases, a Level 2 charger at home is sufficient.
Charging Costs
Charging costs at home depend on the battery size in your vehicle and your local electricity rates.
We will do some simple math to illustrate how to estimate the cost of each fill up.
- Battery size: 60kWh
- Electricity cost: 12c/kWh
- Approximate cost: 60kWh x $0.12/kWh = $7.20
The amount you’re charged at a DC Fast Charger (Level 3) largely differs based on the local government’s policies. In some areas, providers aren’t able to meter electricity which means billing is dependent on how long the vehicle is plugged into the charger.
Rates between states can be found easily enough on Electrify America’s website.
- Battery size: 60kWh
- California Electricity Cost: $0.31/kWh
- Approximate cost: 60kWh x $0.31/kWh = $18.60
Another example where the cost is measured by how long the vehicle is plugged in.
- Battery size: 60kWh
- Texas Electricity Cost: 90 kW at $0.12/min
- Approximate cost: 60kWh / 90kw = 40 minutes; 40min x $0.12/min = $4.80
It should be noted that the calculations above are largely theoretical. All chargers do not have 100% efficiency meaning that the charging speed will be slower than expected. The charge rates also vary depending on the battery state. Batteries need to be at an optimal temperature at 20% to 80% charge to achieve maximum charging rate.
Conclusion
There’s no doubt that electric vehicle technology has come a long way in recent years. The availability of different types of EV chargers makes it easier for drivers to charge their EVs wherever they go. However, it is important to remember that not all chargers are the same and each type of charger has its own set of advantages and disadvantages.
For those who drive an electric vehicle, determining which type of charger works best in your situation is a must before investing any money.
Luckily, there are plenty of resources available online to help you make an informed decision. From budget-friendly chargers for home use to fast charging stations for public places, there is something out there that suits everyone’s needs and lifestyle. So go ahead and start exploring the different types of EV chargers today! [mks_icon icon=”fa-pagelines” color=”#81d742″ type=”fa”]







